- Blog , Cyber Security
- Published on: 14.11.2024
- 10:46 mins
Effective Risk Management Process for Information Security
How to Protect Your Business From Cyber Risks and Operational Downtime
Thanks to globalization and digitalization, companies optimize their operations, reduce lead times and increase flexibility and adaptability, thereby enhancing customer value and company profits. However, the accompanying changes in organizational structure, especially in the IT/OT environment, and dependencies also pose significant risks. Due to modernization, cyber incidents and business interruptions are the greatest business risks for about 70% of companies.
For this reason, an effective and well-implemented risk management process for information security is crucial. Risks can be identified early, appropriate measures can be taken, and damages can be avoided or minimized. This enables your company to benefit from increased planning certainty and significantly reduce fluctuations in cash flow/profit ratios.
In this blog post, you will learn about the individual risks companies face, the benefits of effective risk management, and how MHP can support you in implementing efficient risk management processes.
Business Risks Are Diverse
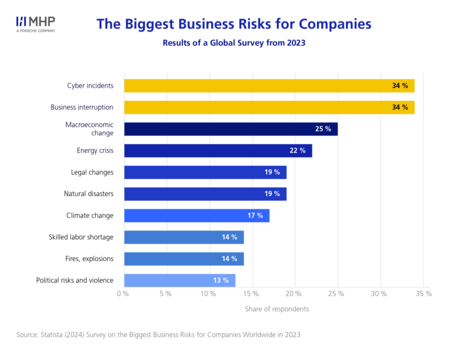
In the modern business world, companies face a wide range of risks that need to be identified, assessed, managed, and monitored. In a representative global survey from 2024, various companies evaluated the risk landscape as follows:
Cyber incidents and business interruptions make up nearly 70 % of the most significant risks. Keep on reading to find out why this is the case.
Cyber Incidents With Enormous Impact
The growing reliance on software solutions and cloud services increases the likelihood that critical systems and processes will be disrupted by cybercrime, software errors, or hardware issues. This can have particularly severe consequences for manufacturing companies in the industrial sector. Below, you’ll learn more about potential risks related to cyber incidents that must be considered within the framework of risk management.
Failure of a critical system due to provider issues
Many companies today rely on cloud services or external IT providers for their IT infrastructure. This poses a potential risk because critical systems may fail due to outages or technical problems on the provider's side. Reasons for such problems can be network issues, server failures, or unscheduled maintenance. This is particularly severe when redundant systems are lacking or emergency plans are inadequate.
System failure due to cybercrime
Cybercrime is one of the biggest threats to IT security. Hacker and phishing attacks or ransomware incidents can compromise systems and significantly disrupt operations. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in IT systems to access sensitive data, encrypt it, or publish it without authorization. For companies in manufacturing, this can lead to the shutdown of entire production facilities. An effective IT cybersecurity strategy helps minimize these risks.
Failures due to bugs
Software bugs can also lead to system failures. Although many companies conduct extensive testing to identify and fix bugs in their software, there is always some residual risk. To mitigate this risk, companies often implement backup systems or fail-safe protocols to reduce the impact of unexpected software issues. However, a critical error can still cause systems to suddenly stop working or malfunction. This is particularly problematic when the supply chain relies on these systems. Manufacturing companies, especially in sectors like automotive or steel, are most often affected by this and benefit greatly from risk mitigation strategies that help maintain operational stability.
Hardware issues
Hardware problems, such as defective or outdated servers, hard drive failures, or other component malfunctions, can also lead to serious outages. Such incidents can occur both in-house and with external service providers. Depending on the importance of the affected hardware, the impact can be significant.
Even Small Business Interruptions Affect Company Operations Greatly
Business interruptions pose a significant threat to the continuity and efficiency of business processes. They can be triggered by various causes, leading to substantial financial losses and damaging a company’s reputation. Effective business continuity planning is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure quick recovery. Two key causes of business interruptions that must be closely considered within risk management and continuity planning are malfunctioning machines and the failure of critical infrastructure, such as water or power supply. Addressing these risks through business continuity strategies helps companies maintain stability and respond swiftly to disruptions.
Defective machines delay operations
In many industries, smooth operations heavily depend on the availability and functionality of machinery. Machines that fail due to technical defects can cause significant delays in production or business processes. These outages are often difficult to predict and especially severe when spare parts or alternative machines are not easily available.
Failure of critical infrastructure such as water or power supply
The availability of essential infrastructure like electricity, water, and other utilities is crucial for the operation of nearly all businesses, especially in manufacturing. A failure of these critical infrastructures can not only halt production but also pose significant safety risks and disrupt the entire business operation.
Failure of production facilities and disruptions in the supply chain
When entire production facilities in a manufacturing company fail, it leads to high costs for repairs and delays in planning, negatively impacting customer trust. In the worst-case scenario, companies lose both current and future orders.
A similar situation arises with supply chains. When these are disrupted by technical issues, cyberattacks, or poor availability, delays occur in logistical processes. The resulting chaos or long waiting times for customers and the company result in costs and losses.
The Benefits of Effective Information Security Risk Management Speak for Themselves
An effective risk management system ensures stability and security by enabling the identification, assessment, and minimization of risks that threaten operations and strategic objectives. The key benefits include crisis preparedness, stabilization of financial processes, risk minimization, and enhanced stakeholder trust. In the complex field of information security, this system serves as a crucial safeguard in an increasingly digital landscape, enabling organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats.
Plans for the worst-case scenario
A successful risk management system ensures that your company is prepared for unexpected events. Emergency plans allow for rapid responses to minimize business interruptions and limit damage.
Benefits:
- Quick resumption of operations after disruptions.
- Structured crisis management based on prepared scenarios.
- Prevention of uncontrolled actions.
Reducing cash flow and profit fluctuations
Risk management helps reduce financial fluctuations by minimizing unexpected expenses through protective measures.
Benefits:
- Improved financial planning and stable cash flow.
- Avoidance of unexpected expenses.
- Enhanced liquidity.
More realistic assessments of capital
By making potential risks visible, risk management enables informed decisions about capital investments. This leads to safer investments and more efficient capital allocation.
Benefits:
- More targeted and secure investments.
- Avoidance of excessive financial risks.
- More sustainable capital utilization.
Security for all stakeholders
A solid risk management system builds trust on all sides. Investors appreciate the increased security of their investments, while customers and employees benefit from reliable business operations.
Benefits:
- Greater trust from investors, making the company more attractive to potential investors.
- Reliability and loyalty from customers.
- Increased job security for employees.
Step by Step to Effective Risk Management
Implementing an effective risk management system, whether for information security or other areas, presents significant challenges for many companies. Given the potential scope of the damage, it is especially important to approach the implementation and establishment in a structured and systematic manner to create and execute a concept perfectly tailored to your company. Below, you find a sample step-by-step process for implementing successful risk management.
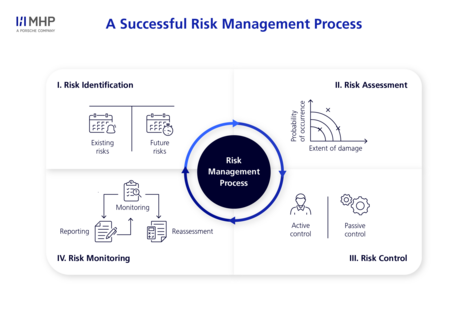
Step 1: risk identification
The first step in risk management is to identify potential risks. Depending on your company structure and industry, different methods can be used for risk analysis.
- Existing risks: To identify known risks, methods such as checklists, workshops, site inspections, interviews, organizational plans, financial statements, and damage statistics can be employed. These help uncover vulnerabilities and recurring risk factors.
- Unexpected or future risks: These can be determined through brainstorming sessions, questionnaires, or scenario analyses. The main focus of this risk analysis is on potential developments that have not yet occurred but could have an impact in the future.
Step 2: risk assessment
After identifying the risks, the next step is to evaluate them. This is done by experts who analyze the likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact of the identified risks. Simple scales are often used for this purpose:
- Likelihood of Occurrence: A scale from 1 to 5 can be applied, where 1 represents a low probability (unlikely) and 5 represents a high probability.
- Impact: The severity of the impact is also rated on a scale, for example, from 1 (minor risk) to 5 (catastrophic risk).
Based on these two assessments, a new scale for the overall risk is created, ranging from 1 (insignificant) to 5 (business-critical). This risk evaluation helps to prioritize and plan targeted actions. Alternatively, other scales can certainly be used. For example, scales ranging from 1 to 10 are also common, as seen in the FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) methodology. It is crucial, however, that consistent assessment criteria are applied throughout the entire risk evaluation process.
Step 3: risk control
In this step, measures to minimize or avoid the prioritized risks are defined and implemented. There are two basic approaches:
- Active Risk Control: Preventive measures are taken to prevent risks from occurring. Examples include security protocols, regular maintenance, or training.
- Passive Risk Control: In this case, the risk is accepted, but precautions are taken to minimize the impact if the risk materializes. These may include emergency plans or insurance policies.
The main focus is preventing unacceptable risks and minimizing unavoidable ones through targeted actions. The specific design of these measures also depends on whether they are operational or strategic. Operational risk management focuses on identifying and controlling risks in day-to-day business operations, such as production failures or security issues. In contrast, strategic risk management deals with long-term risks that affect the company’s strategy and goals, such as market changes or technological disruptions.
Step 4: risk monitoring
Once risks have been identified, assessed, and managed, it’s crucial to continuously monitor them. Changes in the market, technology, or the business environment may necessitate a re-evaluation and adjustment of risks. As part of ongoing reporting, regular risk management reports are sent to relevant stakeholders. These reports provide a transparent overview of the current risk status and assist decision-makers in making timely adjustments.
Furthermore, these reports ensure transparency for stakeholders and contribute to a better understanding of the overall risk assessment.
MHP Supports You in Implementing a Tailored Information Security Risk Management System
When it comes to the complex integration of a functional and company-specific information security risk management system based on ISO/IEC 27005 or IEC 62443-3-2, MHP is here to assist you.
With years of experience and extensive expertise in information security management, we support your company in implementing an effective and sustainable risk management system. Our approach is practical and covers the entire risk management process – from identifying potential risks to the continuous monitoring and adjustment of measures.
End-to-end risk management
MHP offers a comprehensive end-to-end concept that integrates all key steps of risk management:
- Risk identification: MHP helps your company systematically capture potential risks. This is done through proven methods such as workshops, checklists, and data analysis.
- Risk assessment: MHP works with you to assess the identified risks based on likelihood and impact, translating them into a clear priority list.
- Risk Control: MHP develops tailored measures to either proactively avoid the identified risks or minimize their impact.
- Risk Monitoring: Through monitoring systems and regular reports, MHP ensures that risks are continuously monitored and reassessed as needed.
Customized approach for maximum effectiveness
Every company has a unique risk landscape. That’s why MHP follows a tailored approach: Based on your company’s specific industry, structure, and strategic goals, concepts are adapted flexibly. This ensures that risk management is optimally aligned with the requirements and challenges of your business.
Minimize Business Risks With a Customized Risk Management Process
Driven by globalization and digitalization, businesses face a wide range of risks. Among the biggest challenges are cyber incidents and operational disruptions, which can lead to significant financial losses and permanently damage a company’s reputation. A well-thought-out risk management strategy for information security is essential to identify, manage, and mitigate these risks early, preventing long-term damage.
Effective risk management offers numerous benefits: It ensures better planning certainty, reduces financial fluctuations, and protects companies from potential disasters. By systematically identifying, evaluating, managing, and monitoring risks, companies are not only prepared for unexpected events but also able to allocate capital investments more effectively and strengthen the trust of customers, investors, and employees.
MHP supports companies with a comprehensive, practical end-to-end approach that is tailored to the specific needs and challenges of each organization. To reduce risks and strengthen cybersecurity, MHP employs a structured approach that includes, among other things, ISO/IEC 27001 for information security, the targeted risk management of ISO/IEC 27005, and the protection measures of IEC 62443 for industrial systems. From identifying potential risks to evaluating and managing them, and finally ensuring continuous monitoring, MHP ensures that companies are optimally prepared for risks and implement sustainable solutions.
FAQ
Risk Management is a systematic process in which potential risks to a company are identified, assessed, and managed through targeted measures. The goal is to minimize or avoid risks to protect the company's objectives and ensure financial stability.
The key steps in a risk management process include identifying risks, evaluating them based on the probability of occurrence and potential impact, implementing measures to minimize or avoid risks, and continuously monitoring the risks. This process helps to detect potential threats early and manage them effectively.
The two primary types of risk management are operational risk management, which addresses day-to-day operational risks, and strategic risk management, which focuses on long-term risks impacting the company’s strategy. Risk management approaches can further be divided into active risk management, involving preventive measures, and passive risk management, which entails measures to mitigate potential damage.